/ Automation / Metrology
Metrology

Ensure the highest precision and quality in manufacturing with advanced metrology using 3D sensors. Verify geometric features and tolerances with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency.

Elevating Precision Manufacturing with Advanced Metrology
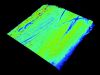
In the realm of precision manufacturing, maintaining stringent quality standards is paramount. Metrology, the science of measurement, plays a crucial role in verifying that each component meets specified geometric features and tolerances. With the integration of 3D sensors, metrology has reached new heights of accuracy and efficiency. This article explores the world of metrology with 3D sensors, highlighting its benefits, applications, and the steps involved in the process.
Benefits of Metrology with 3D Sensors
-
Unmatched Accuracy3D sensors provide highly accurate measurements, ensuring that every component meets precise specifications and quality standards.
-
Enhanced EfficiencyAutomated measurements with 3D sensors speed up the inspection process, reducing downtime and increasing throughput in manufacturing.
-
Early Detection of IrregularitiesMetrology with 3D sensors allows for the early identification of deviations from target values, preventing defects and ensuring consistent product quality.
-
Comprehensive Data CollectionThe detailed data captured by 3D sensors enable thorough analysis and documentation, supporting quality control and continuous improvement efforts.
-
Versatile Application3D sensor-based metrology can be applied to a wide range of materials and components, making it suitable for various industries and applications.
By leveraging the advanced capabilities of C6 3D sensor, metrology ensures that manufacturing processes meet the highest standards of precision and quality, contributing to overall productivity and cost savings.
Metrology: Who Needs It, When to Apply It, and Where It Works Best
Application Examples
What is Metrology?
Metrology is concerned with measuring objects to determine their geometric features such as size, shape, and volume. Every product is manufactured according to a specification that sets certain tolerances the component must meet to comply with quality standards. Using metrology, AT verifies these tolerances and compares them with the information from the technical drawing to ensure that all components meet the specified quality requirements.
By integrating 3D sensors, metrology enhances the precision and efficiency of these measurements. This advanced technology allows for a detailed comparison between the manufactured component and its technical specifications, ensuring compliance with quality standards and detecting any deviations early in the process. Some important Use Cases for Metrology:
-
Dimensional InspectionUsing 3D sensors, metrology verifies the exact dimensions of components, ensuring they meet design specifications and tolerances.
-
Geometric AnalysisMetrology evaluates the geometric features of objects, such as flatness, roundness, and angles, to ensure they conform to the required standards.
-
Volume MeasurementIn industries like packaging and logistics, metrology with 3D sensors accurately measures the volume of objects for optimized space utilization and material usage.
-
Surface AnalysisMetrology inspects surface roughness and texture, which is crucial for components that require specific surface finishes for functionality or aesthetics.
-
Assembly VerificationBy measuring assembled components, metrology ensures that all parts fit together correctly and function as intended, preventing assembly issues and enhancing product reliability.
How Metrology Works:
5 Simple Steps
Metrology with 3D sensors is a precise and systematic process.
Here’s how it works:
Here’s how it works:

1. Component Scanning
The component is scanned by our 3D sensors, capturing detailed geometric data and creating a comprehensive 3D model.

2. Data Processing
The scanned data is processed and inspected using advanced metrology libraries, comparing the measured values with reference values from technical drawings.

3. Deviation Analysis
During the inspection process, any deviations from the target values are identified and precisely analyzed, highlighting potential irregularities.

4. Quality Assurance
The analysis ensures that all components meet the specified quality requirements, verifying that they comply with the established tolerances.

5. Data Evaluation
Detailed measurements are made, documenting the inspection results and providing valuable data for quality control and process improvement.
By following these steps, metrology with C6 3D sensors ensures the accuracy and quality of every component, enhancing overall manufacturing precision and reliability.
3D sensors for industrial Metrology
Get the most out of your production!
🇺🇸 North America
🇩🇪 Worldwide